Historique de la page
| Sv translation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
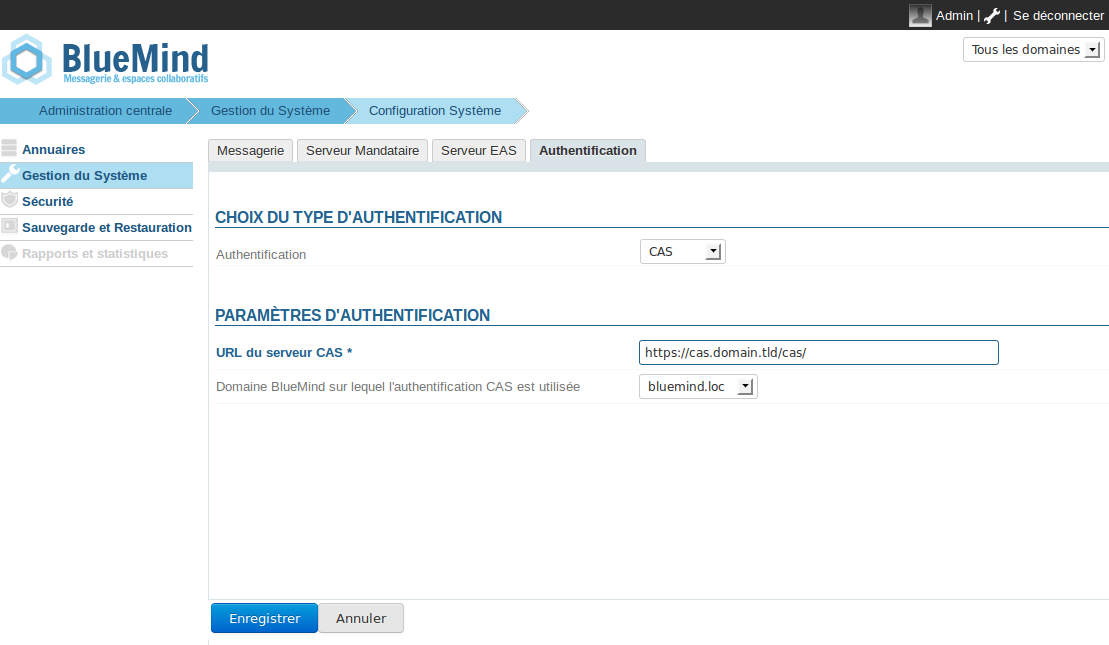
Depuis l'interface d'administration
Configuration de BlueMind à la mainAjouter les lignes suivantes à la fin du fichier :
Fonctionnement de l'authentification CAS
InstallationPour mettre en œuvre l'authentification CAS, installer le paquet nécessaire :
Puis redémarrer BlueMind :
Configuration
Erreurs connuesErreur 403 : Your user account does not exist in this BlueMind.Ce message d'erreur signifie que le login avec lequel l'utilisateur s'est authentifié sur le CAS n'existe pas dans le domaine domain.tld. Deux solutions se présentent à vous :
Erreur 500 : Internal Server ErrorCe message d'erreur peut provenir de plusieurs sources. Le plus simple est d'aller voir sur votre serveur les logs de HPS, en utilisant par exemple la commande suivante :
Utilisation d'un certificat auto-signé ou d'une autorité de certification inconnueSi vous utilisez un certificat auto-signé pour votre serveur CAS, ou que l'autorité de certification de votre serveur CAS n'est pas répertoriée, vous allez sûrement connaître une erreur lors de l'établissement de la connexion https vers le serveur CAS. Pour résoudre cette erreur, le plus simple est d'importer le certificat en question dans le keystore de la jvm qu'utilise BlueMind.
|
| Sv translation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bm_infotraduction|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
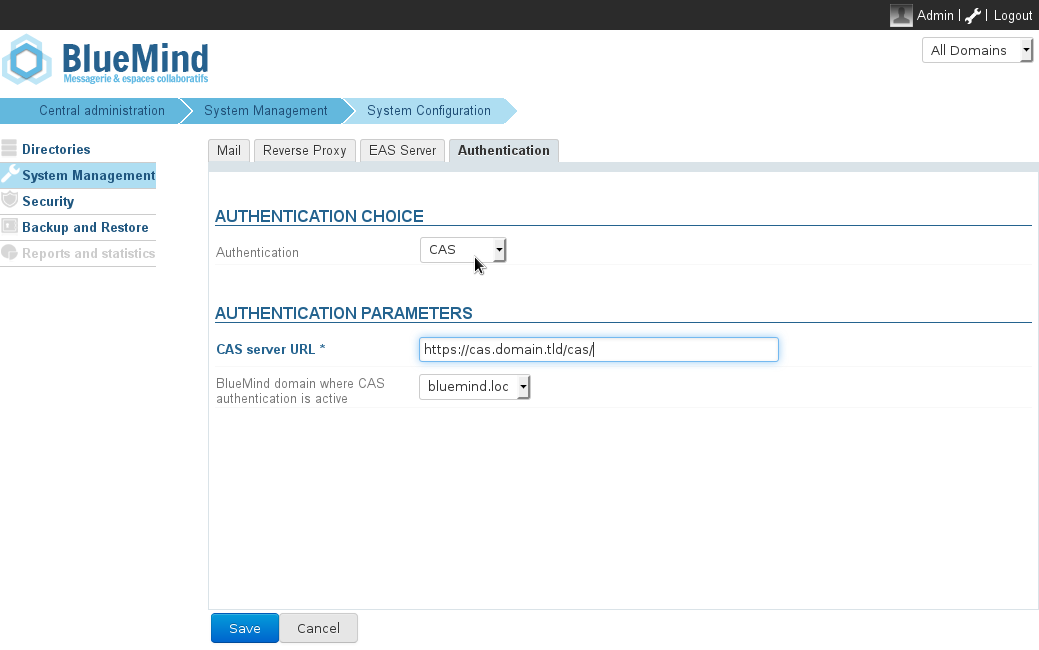
Setting up CAS in the admin console
Setting up CAS manuallyAdd the following command lines at the end of the file:
How CAS authentication works
InstallationInstall the needed package :
Restart BlueMind :
Configuration
Known errorsError 403: Your user account does not exist in this BlueMind.This error message means that the username entered to authenticate on the CAS does not exist in the domain domain.tld. You have two options:
Error 500: Internal Server ErrorThis error message can have several causes. The easiest way to find out is to look at your server's HPS logs, using the command below, for instance:
Using a self-signed certificate or an unknown certification authorityIf you use a self-signed certificate for your CAS server, or your CAS server's certification authority is not indexed, you will probably get an error message when you connect to the CAS server via https. The easiest way to resolve this error is to import the certificate into the jvm keystore BlueMind uses.
|